The calculation of the influence of overloads arising during the movement of the carrier platform on the operation of the phased antenna arrays (PAA) placed on it was carried out by scientists of the Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology (MIPT) together with Moscow State students. Technical University (MSTU). NE Bauman, on May 2, reports the MIPT magazine “For Science”.
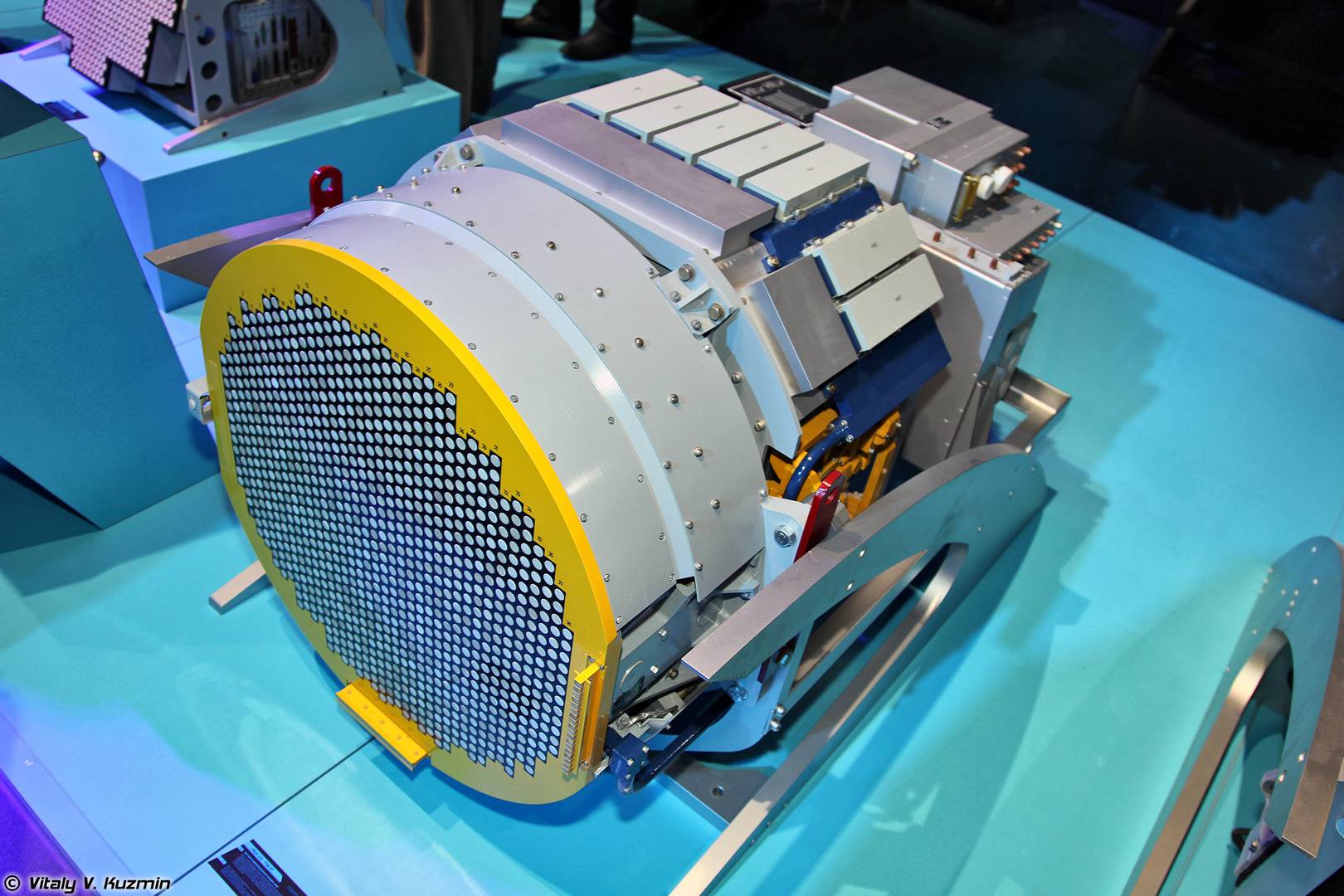
PAR (phase array antennas) are used in devices to receive and transmit electromagnetic signals. Structurally, they consist of the same type of radiating elements (antennas), arranged in a certain order.
Their peculiarity is that they allow the direction and power of the electromagnetic waves emitted or received to be controlled without changing their own geometry. This property allows them to communicate simultaneously in many directions or track multiple fast-moving objects.
Beacons are used in the design of radio telescopes, radar stations, mobile telephone base stations, satellite communication systems and many other devices. They are installed on various mobile platforms, including cars, locomotives, airplanes, drones and spacecraft.
Moscow scientists in their work investigated the effects that arise during the operation of phased antenna arrays specifically installed on mobile media when the platform accelerates. As a result, they obtained data on the deformations to which these systems are subjected to overloads, and the corresponding distortions in the antenna radiation pattern.
The authors presented the calculations carried out using an innovative technique in the report “Study of the operation of phased arrays under time-varying overloads” at the VI International Youth Conference on Radioelectronics, Electrical Engineering and Energy (REEPE), published in the proceedings congressional.
Based on the results of the calculation, requirements were formulated for the material from which phased antenna arrays are manufactured, as well as recommendations for their installation and mounting on supports. Compliance with the recommendations will ensure a 60-70% reduction in the impact of overloads, and this will lead to an increase in the service life of devices without significantly complicating their design.
One of the authors of the scientific work, head of the department of applied research and development of advanced cellular communication solutions of the MIPT Telecommunications Research Center, Grigory Seregin, spoke about the research:
“Initially we used a software package to simulate the changes that occur in the system during mechanical loading. In general terms, how the network bends under the influence of forces that arise during the application of acceleration. Then, using another program, we observe what processes occur from the point of view of electrodynamics, that is, how the characteristics of the antenna radiation pattern change.”.
From this data, the researchers developed a methodology to calculate changes in the operating parameters of the phased system, including a decrease in antenna gain for a given load. In addition, the process of changing the operating frequency range of the antenna system was analyzed, which occurred due to changes in the geometric configuration of its individual elements caused by overload.
Taking these dynamic processes into account at the design stage will help designers create reliable antenna systems without excessive safety margins. This will reduce the weight of the structure, which is important for aviation and astronautics.
Among other things, modeling using the developed methodology will help find the optimal solution for mounting phased antennas on a spacecraft or on an aircraft in such a way that during moments of maximum overload the structural integrity and functional properties of the antenna are preserved. phased array. .
Source: Rossa Primavera
I am Michael Melvin, an experienced news writer with a passion for uncovering stories and bringing them to the public. I have been working in the news industry for over five years now, and my work has been published on multiple websites. As an author at 24 News Reporters, I cover world section of current events stories that are both informative and captivating to read.
